NPAPI is a Netscape plugin development platform, recently supported by many browsers. Allowed to expand the functionality, view various content directly from the program window. Such plugins as Adobe Flash Player, Unity, Java, Silverlight and many others work on it.

NPAPI support must be enabled on Opera and Firefox browsers
The refusal is justified by the fact that the plug-ins posed a serious potential danger to the computer, since they were run with parental rights and often viruses and malware penetrated under their guise. They also slow down the browser and sometimes lead to critical errors.
Nevertheless, many sites work with this technology, therefore, at the request of users, browsers have the ability to enable platform support.
Mozilla firefox
The Firefox browser uses add-ons to implement functions that it cannot perform. These are usually audio, video, online games, presentations, web conferences, and more. Firefox supports the following plug-ins:
- Adobe Flash;
- Java - view the interactive content of the site;
- Silverlight - play video and audio;
- QuickTime - play audio and video;
- Windows Media - playing WinMedia;
- Adobe Acrobat - open and view PDF documents.
The 64-bit version of Firefox only supports Adobe Flash and Silverlight. Starting from version 52, Firefox browser has stopped supporting all add-ons except for Adobe Flash. During the transition period of abandoning the technology, the company released the Firefox ESR (Extended Support Release) browser with support for the Netscape platform until the beginning of 2018.

As an alternative, Firefox offers WebApi technology. Many sites have now begun to switch to new platforms, and the need for old unsafe add-ons disappears. However, you can turn them on and off as needed:
- Click the Menu button and select Add-ons.
- On the Manage tab, select Always Enable.
With Firefox 52 and above, support is limited, so to enable it, do the following:
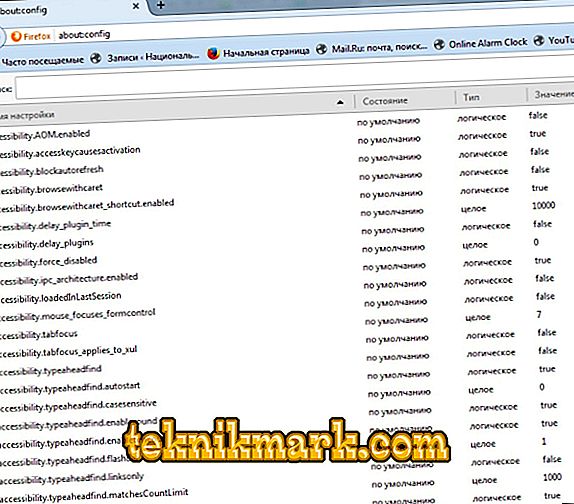
- Open a browser and in the new tab as the address enter about: config.
- Confirm the intention.
- Add a boolean variable plugin.load_flash_only.

- Set the variable to false.
- Restart the browser.
With Firefox 53, the ability to enable NPAPI support will be completely excluded from the program code.
Opera
Opera also uses plugins to extend its functionality:
- to display flash content;
- to communicate with third-party applications;
- to support special web functions.
View the available plug-ins in Opera browser as follows:
- Type opera: plugins in the address bar.

- A list appears with the names, type and location of the location.
Starting with Opera 36, NPAPI support has been disabled, so Opera, following the leading programs, has stepped on the path to transition to new technologies. However, unlike Firefox, they left the ability to enable plugins support. And also in the new version of Opera PPAPI Flash is used. This is a new interface that has no such security and performance issues. However, while it is not working on all sites correctly. If you have problems with flash content, change the type as follows:
- Go to Opera in the "Menu", select "Other Tools", then "Enable Developer Tools".

- The line “Developer Tools” will appear in the Menu, select “Plugins” in it.
- Locate the Adobe Flash Player, “Show Details.”
- Disable PPAPI type and enable NPAPI.
You can enable technology support in Opera via the enable npapi command:
- Open a browser and enter opera: // flags in the address bar.
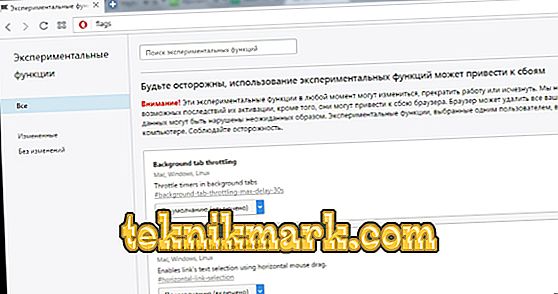
- In the search bar, type npapi.
- In the Disable NPAPI plug-ins found, select
The same can be done with the chrome: // flags / # enable-npapi command. After that, restart the program.
Thus, while it is possible to bypass the restriction of Firefox and Opera to use NPAPI. But remember that such actions threaten the stability and security of the program and the computer as a whole. After all, it is not for nothing that leading developers abandon this technology, limit its use for the transitional period, until web programmers reconfigure their sites for a new reality.





